Whortleberry
Closely related to Blueberries
Botanical name: Vaccinium myrtillus
Family: Heath (Ericaceae)
Collectability: good, specialised habitat
Main benefit
 antioxidants, strengthens blood vessels
antioxidants, strengthens blood vessels
Use - overview








Features and Identification
Habitat
Type: woods, moors
Distribution: throughout northern hemisphere
Prefers: acid soil
Other: not on lime, patch forming
General
Growth type: shrub
Cycle: deciduous
Height: up to 50 cm
Other: hairless
 Leaf
Leaf
Shape: oval
Arrangement: alternate
Edge: finely toothed
Other: small
 Stem
Stem
Cross Section:angular
 Flower
Flower
Shape: bell
Diameter: 6 mm
Arrangement: single or paired
When: April to July
Colour:
 Fruit
Fruit
Shape: round
Colour: blue-black
Size: up to 10 mm
Other: purplish bloom
Type: woods, moors
Distribution: throughout northern hemisphere
Prefers: acid soil
Other: not on lime, patch forming
General
Growth type: shrub
Cycle: deciduous
Height: up to 50 cm
Other: hairless
 Leaf
LeafShape: oval
Arrangement: alternate
Edge: finely toothed
Other: small
 Stem
StemCross Section:angular
 Flower
FlowerShape: bell
Diameter: 6 mm
Arrangement: single or paired
When: April to July
Colour:

 Fruit
FruitShape: round
Colour: blue-black
Size: up to 10 mm
Other: purplish bloom
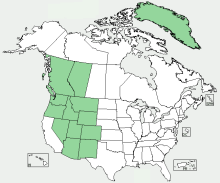
Distribution Map
Caution Notes
 the leaves should only be consumed up to three weeks at a time
the leaves should only be consumed up to three weeks at a time
When Available?
 September and October
September and October July to September
July to SeptemberParts with black and white icons are for non-culinary use
Culinary Use
Flavour
Rating and Description:

 mildly sweet-sour
mildly sweet-sour
How to Consume
 tea
tea
 raw, dried
raw, dried
Nutrition
 glucoquinones - reduces blood sugar levels
glucoquinones - reduces blood sugar levels
 (skin) anthocyanin, anthocyanosides
(skin) anthocyanin, anthocyanosides
Used as ...
 beverage
beverage
 food
food
Rating and Description:

 mildly sweet-sour
mildly sweet-sourHow to Consume
 tea
tea raw, dried
raw, driedNutrition
 glucoquinones - reduces blood sugar levels
glucoquinones - reduces blood sugar levels (skin) anthocyanin, anthocyanosides
(skin) anthocyanin, anthocyanosidesUsed as ...
 beverage
beverage food
food
Medicinal Use
Action:
 antiseptic (urinary tract), astringent, diuretic, tonic,
antiseptic (urinary tract), astringent, diuretic, tonic,
 fresh: laxative; dried: antibacterial, astringent; berry skin: vasodilator
fresh: laxative; dried: antibacterial, astringent; berry skin: vasodilator
May treat:
 diabetes (if taken for prolonged period; not replacing conventional treatment); external: ulcers, ulceration of mouth or throat
diabetes (if taken for prolonged period; not replacing conventional treatment); external: ulcers, ulceration of mouth or throat
 fresh: diarrhoea; berry skin: varicose veins, haemorrhoids, capillary fragility, improves night vision, circulation and memory
fresh: diarrhoea; berry skin: varicose veins, haemorrhoids, capillary fragility, improves night vision, circulation and memory
 antiseptic (urinary tract), astringent, diuretic, tonic,
antiseptic (urinary tract), astringent, diuretic, tonic,  fresh: laxative; dried: antibacterial, astringent; berry skin: vasodilator
fresh: laxative; dried: antibacterial, astringent; berry skin: vasodilatorMay treat:
 diabetes (if taken for prolonged period; not replacing conventional treatment); external: ulcers, ulceration of mouth or throat
diabetes (if taken for prolonged period; not replacing conventional treatment); external: ulcers, ulceration of mouth or throat fresh: diarrhoea; berry skin: varicose veins, haemorrhoids, capillary fragility, improves night vision, circulation and memory
fresh: diarrhoea; berry skin: varicose veins, haemorrhoids, capillary fragility, improves night vision, circulation and memory
Other Use
 green dye
green dye blue or black dye/ink
blue or black dye/ink
Collection, Storing and Notes
Collection
 only green leaves
only green leaves
 hidden under leaves
hidden under leaves
Drying
 dry in gentle heat
dry in gentle heat
 in shade
in shade
Note
indicates acid soil
 only green leaves
only green leaves hidden under leaves
hidden under leavesDrying
 dry in gentle heat
dry in gentle heat in shade
in shadeNote
indicates acid soil
Key
Plant parts:
 leaf
leaf
 stem or trunk
stem or trunk
 sap
sap
 root, bulb, tuber and other below ground parts
root, bulb, tuber and other below ground parts
 flower
flower
 fruit
fruit
 seed
seed
Parts with black and white icons in the availability section are for non-culinary use
Use:
 culinary use
culinary use
 medicinal use
medicinal use
 household use
household use
Other:
 caution
caution
 leaf
leaf stem or trunk
stem or trunk sap
sap root, bulb, tuber and other below ground parts
root, bulb, tuber and other below ground parts flower
flower fruit
fruit seed
seedParts with black and white icons in the availability section are for non-culinary use
Use:
 culinary use
culinary use medicinal use
medicinal use household use
household useOther:
 caution
caution
Glossary
Glossary of Medicinal Terms and Nutritive Substances
- anthocyanin: antioxidant, mostly in skin of dark blue fruit or red leaves; improves night vision, circulation, memory
- anthocyanosides: antioxidant; strengthens capillaries/connective tissue; may improve night vision
- antibacterial: kills bacteria
- antiseptic: prevents putrefaction (applied to wounds)
- astringent: causes localised contraction of blood vessels and tissue, reducing the flow of blood, mucus, diarrhoea etc.
- diuretic: increases secretion and elimination of urine
- glucoquinones: reduce blood sugar levels
- laxative: evacuates the bowels or softens stools
- tonic: improves general health, bringing steady improvement
- vasodilator: widens blood vessels, reducing blood pressure




